STOP THE TABOO.......
-
Prostate cancer
For most men having an invasive prostate exam which entails the insertion of the doctor’s finger into the patient’s rectum to feel for bumps and abnormalities in the prostate gland is emasculating and humiliating.
At age 40 it is recommended that men have a Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) test done. This test offers a rating from 0.0 to 0.4 as safe from cancer. A rating over four would result in the patient being urged to have a rectal ultrasound done and subsequent biopsy.
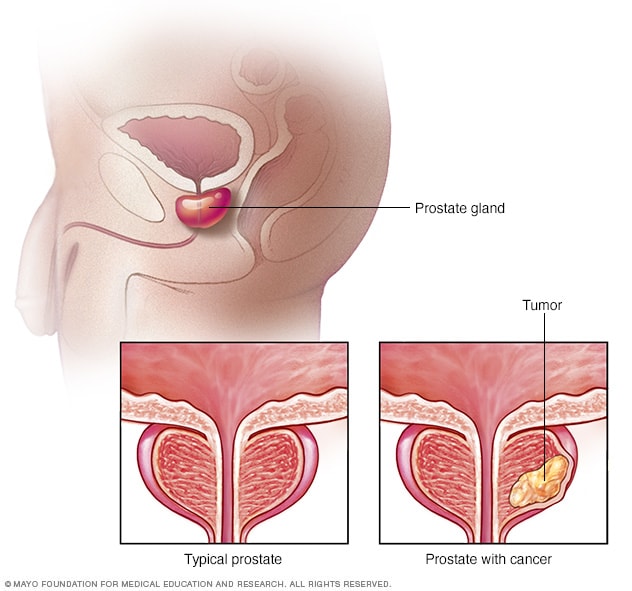
Prostate cancer is cancer that occurs in the prostate — a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces the seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men. Usually, prostate cancer grows slowly and is initially confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. However, while some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or even no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly.
Prostate cancer that's detected early — when it's still confined to the prostate gland— has a better chance of successful treatment.
Symptoms
Prostate cancer may cause no signs or symptoms in its early stages.
Prostate cancer that's more advanced may cause signs and symptoms such as:
- Trouble urinating
- Decreased force in the stream of urine
- Blood in semen
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
- Bone pain
- Erectile dysfunction
Factors that can increase your risk of prostate cancer include:
- Age. Your risk of prostate cancer increases as you age.
- Race. For reasons not yet determined, black men carry a greater risk of prostate cancer than do men of other races. In black men, prostate cancer is also more likely to be aggressive or advanced.
- Family history. If men in your family have had prostate cancer, your risk may be increased. Also, if you have a family history of genes that increase the risk of breast cancer or a very strong family history of breast cancer, your risk of prostate cancer may be higher.
- Obesity. Obese men diagnosed with prostate cancer may be more likely to have advanced disease that's more difficult to treat.
SET AN APPOINTMENT TODAY!
DON'T DELAY!
CALL: 235-5066

Comments
Post a Comment